Did you know that, according to a study by Gartner, the worldwide public cloud service market is projected to grow 17.5% in 2019 to total $214.3 billion, up from $182.4 billion in 2018?
You’re probably aware that cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering them unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. But, do you understand the technical aspects that make all this possible?
As you navigate through this intricate world of virtual servers, storage, and applications, you’ll uncover how these technological elements seamlessly work together.
Let’s begin this exploration, shall we?
Key Takeaways
- Cloud computing delivers computing services over the Internet, reshaping the way businesses manage data and IT resources.
- Virtualization is a core element of cloud infrastructure, allowing for the abstraction of physical hardware and the efficient utilization of resources.
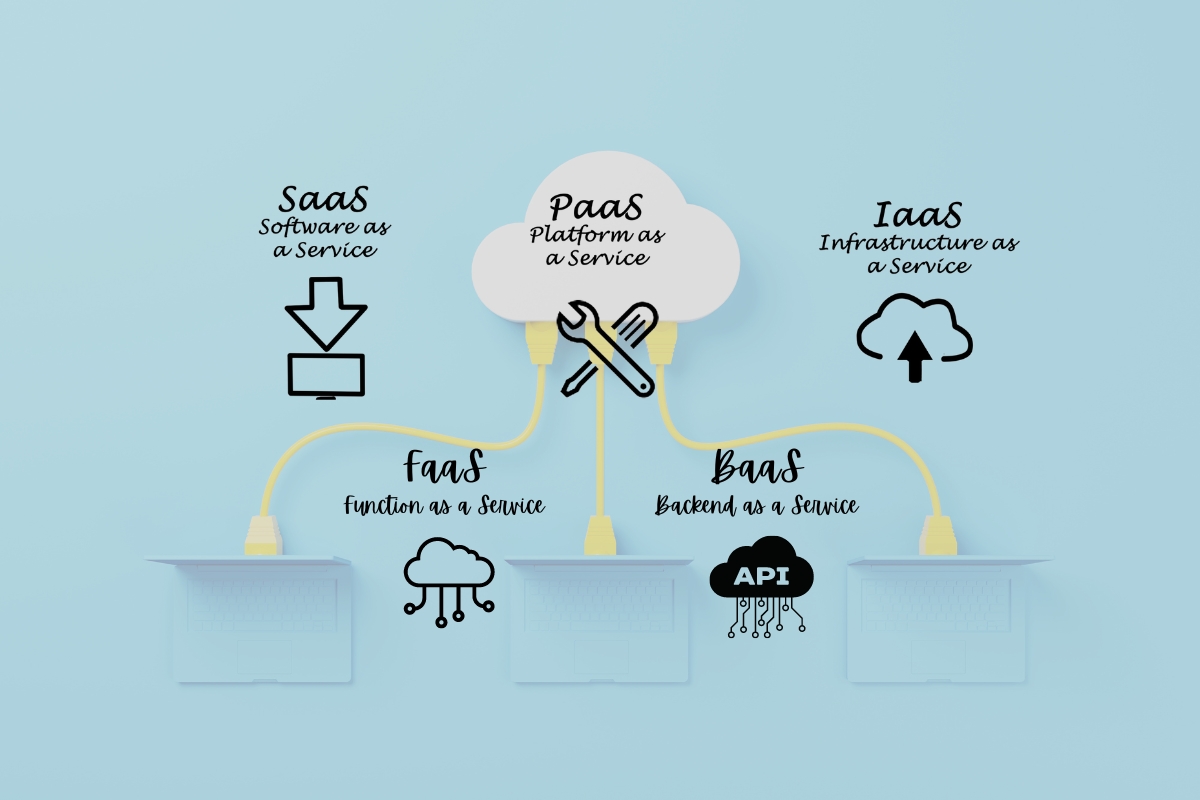
- Different cloud service models, such as IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, FaaS, and BaaS, offer varying levels of functionality and flexibility.
- Security measures, such as encryption techniques and addressing data breaches promptly, are crucial for protecting data in a shared hardware environment.
Understanding Cloud Computing Basics
As you delve into the basics of cloud computing, it’s essential to understand that it’s a technology which delivers a wide array of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the Internet. This technology is fundamentally reshaping the way businesses manage data and IT resources.
Cloud computing allows for quicker innovation and flexible resources. You’re essentially renting access to software and storage from cloud service providers, which can lead to economies of scale. Any service that doesn’t need you to be physically close to the computer hardware can be delivered via the cloud. This includes a range of services from Gmail, cloud backup and enterprise data hosting to Netflix streaming.
However, it’s crucial to be aware of the new costs and risks this technology introduces. While security breaches are relatively rare, concerns about the security of cloud services still exist. Different models of cloud computing—public, private, and hybrid—offer varying degrees of security, scalability, and control over data and services. Understanding these nuances can help you leverage cloud computing to its full potential.
Core Elements of Cloud Infrastructure
Now that you’ve grasped the basics of cloud computing and its different models, let’s explore the core elements of cloud infrastructure, which include virtualization, scalability, and elasticity.
These elements are key components of Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), a primary service model of cloud computing.
- Virtualization: This is the abstraction of physical hardware, allowing multiple users to utilize the same resources. It forms the compute and storage infrastructure of cloud services.
- Scalability: Cloud providers such as Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud offer the ability to scale resources up or down as per your needs, ensuring cost-effectiveness and efficiency.
- Elasticity: This provides the capability to quickly expand or reduce resources to meet demand. It enables rapid expansion during peak usage and contraction during off-peak times.
These core elements work synergistically to optimize your cloud infrastructure’s performance, ensuring that you have the necessary resources when you need them. They form the backbone of IaaS, contributing to the flexibility and cost savings associated with cloud computing.
Exploring Different Cloud Service Models
Diving into the realm of cloud service models, you’ll encounter various forms such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), Function as a Service (FaaS), and Backend as a Service (BaaS), each designed to cater to specific parts of the technology stack and unique use cases.
For instance, IaaS are used to offer rented physical or virtual servers, storage, and networking. Azure Services, a leading player in the public cloud, excels in providing robust IaaS solutions. On the other hand, PaaS, like Google’s App Engine, provides tools and software for application development, allowing developers to focus on coding rather than infrastructure management.
| Service Model | Typical Use |
|---|---|
| IaaS | Renting Servers, Storage |
| PaaS | App Development |
| SaaS | Delivering Software over the Internet |
| FaaS | Event-driven computing |
| BaaS | Backend functions for mobile or web applications |
In terms of deployment model, you can choose between public cloud, private cloud, or a hybrid cloud, depending on your specific needs. By 2025, over 85% of organizations are predicted to embrace a cloud-first principle as cloud computing allows organizations to optimize costs, improve agility, and drive innovation.
The Role of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Now, let’s turn to the role of virtualization in cloud computing.
You’ll see how different types of virtualization contribute to cloud services, the benefits they bring, and the challenges they pose.
Understanding these aspects will help you fully grasp how virtualization forms the backbone of efficient and flexible cloud infrastructure.
Virtualization Types in Cloud
In cloud computing, understanding the role of virtualization is pivotal. There are distinct types of virtualization, each offering unique benefits and use-cases.
- Full Virtualization allows you to run multiple operating systems on a single host. This boosts the scalability and reliability of your computing infrastructure.
- Para-Virtualization is defined by modifications to the guest operating system. These modifications enhance the speed and performance of computing via cloud computing.
- Hardware-Assisted Virtualization utilizes hardware features for improved performance. This increases the efficiency of accessing servers and data.
These virtualization types in cloud computing are key components of cloud computing. Each type is tailored to different needs and applications. Understanding these types can help you optimize your cloud computing experiences.
Benefits of Virtualization
Having explored the different types of virtualization in cloud computing, let’s examine how these techniques enhance the efficiency and functionality of cloud services.
Virtualization allows for efficient utilization of physical IT resources. It consolidates multiple servers into virtual ones, reducing the need for hardware, leading to cost and power savings.
Cloud uses this to offer flexible resources for data storage and computing. Unlike traditional computing, users can access services offered, regardless of their location.
In terms of disaster recovery, virtualization enables quick replication and recovery. It also facilitates better resource management and improved deployment speed.
You only pay for the resources you use, making it a cost-effective choice.
Challenges in Cloud Virtualization
While cloud virtualization offers numerous benefits, it’s not without its challenges. These challenges include performance overhead, security concerns, management complexities, compatibility issues, and potential resource allocation problems.
- Performance Overhead: The extra computing power necessary to run the virtualization layer can impact the speed of your cloud applications, causing delays in your cloud data processing.
- Security Concerns: In a shared hardware environment, your cloud storage and separate cloud data could be exposed to breaches, putting your computing security at risk.
- Management Complexities: Monitoring and optimizing a virtualized compute cloud for performance and resource utilization can be complex and time-consuming.
Understanding these technical aspects of cloud computing is crucial for overcoming the challenges in cloud virtualization and fully leveraging the benefits of this technology.
Security Measures in Cloud Computing
As you venture further into the technical aspects of cloud computing, it’s time to tackle the crucial area of security measures.
Specifically, we’ll discuss how implementing encryption techniques can enhance data protection, and how addressing data breaches promptly and effectively is paramount.
Understanding these elements is vital in maintaining the integrity and security of data in a cloud computing environment.
Implementing Encryption Techniques
To bolster security in cloud computing, you need to implement encryption techniques, ensuring your data remains confidential and inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. When using cloud services for storing information or hosting software-as-a-service applications, implementing encryption techniques is pivotal to safeguard your sensitive or corporate data.
Here’s a brief overview of the process:
- Choose an appropriate encryption method, like symmetric or asymmetric encryption, hashing, or digital signatures.
- Encrypt your data before it’s stored in the cloud.
- Manage your encryption keys diligently. They’re essential for decrypting your data when needed.
Addressing Data Breaches
In addressing data breaches, you need to take robust security measures in your cloud computing environment to protect sensitive data and mitigate potential threats.
Cloud computing refers to the use of hardware and software resources over an internet network link. It offers the ability to spin up applications and services as per use cases, but it can be less secure.
You must implement encryption, tokenization, and multi-factor authentication to enhance access control. Regularly monitor and audit your cloud to detect vulnerabilities. Use data loss prevention tools and establish clear procedures for incident response and data breach notification.
This can help minimize damage from cloud outages and keep your cloud operations secure.
Future Trends in Cloud Technology
Diving into the future of cloud technology, you’ll see a marked shift towards serverless computing, edge computing, multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, advancements in security, and the integration of AI and machine learning. The compound annual growth rate of cloud computing is set to skyrocket, making this a critical area to understand.
Cloud computing trends can be divided into three major areas:
- Serverless and edge computing: With the new cloud paradigm of serverless computing, you’re able to access top cloud services without worrying about server management. Additionally, edge computing is meeting the demand for computing resources close to data sources, enhancing real-time responses.
- Multi-cloud and hybrid strategies: Businesses are adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies to optimize costs and performance. This approach offers flexibility and decreases dependency on a single provider.
- Security and AI integration: The future of cloud computing also includes significant advancements in security protocols to protect data via cloud computing. Furthermore, the introduction of AI and machine learning in cloud platforms enables efficient automation and insightful predictive analytics.
The future of cloud technology is dynamic and filled with potential. Stay ahead by understanding these trends and harnessing their capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Technical Description of Cloud Computing?
You’re essentially asking about the structure of cloud computing. It’s a tech model allowing on-demand network access to shared resources, including servers, storage, and applications, without direct management by the user.
What Are the Technical Requirements for Cloud Computing?
You’ll need virtualization technology, robust data storage, and backup solutions. Scalability and elasticity are also essential, as is automation for efficient management. Lastly, APIs are required for seamless integration and simplifying complex services.
What Are the Technological Factors of Cloud Computing?
The technological factors of cloud computing you’ll consider include virtualization, scalability, APIs, microservices, and infrastructure. They’re vital for on-demand access, real-time data streaming, and IoT device empowerment. Don’t overlook the role of software too.
What Are the Essential Technical Characteristics of Cloud Computing?
You’re looking at key characteristics like virtualization, scalability, and elasticity. They’re crucial for on-demand access, cost savings, and data storage. Also, infrastructure tech, software, APIs, and storage play significant roles in cloud computing’s functionality.
Conclusion
In sum, you’ve delved into the technical aspects of cloud computing, understanding its basics and core infrastructure. You’ve explored service models, the role of virtualization, security measures, and future trends.
APIs, virtualization, and other technologies give you access to cost-effective, flexible, and efficient cloud services. Keep abreast of these trends to leverage the full potential of cloud technology in your organization.
Remember, cloud computing isn’t just about saving money, it’s about driving innovation.